A cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses cryptography to secure the transactions, control the creation of additional units, and to verify the transfer of assets due to which it is difficult to counterfeit.
A defining feature of a cryptocurrency, and arguably its most endearing allure, is its organic nature. It uses decentralized control which means it is not issued by any central authority (as opposed to centralized banking and economic systems such as the Federal Board of Revenue or Federal Reserve System), rendering it theoretically immune to government interference or manipulation. The anonymous nature of cryptocurrency transactions makes them well-suited for a host of nefarious activities, such as money laundering and tax evasion.

As of June 2017 total market capitalization of cryptocurrencies is bigger than 100 billion USD and record high daily volume is larger than 6 billion USD.
Bitcoin – First Cryptocurrency
The first cryptocurrency to capture the public imagination was Bitcoin, which was launched in 2009 by an individual or group known under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. Since then numerous cryptocurrencies have been created called altcoins. As of September 2015, there were over 14.6 million bitcoins in circulation with a total market value of $3.4 billion. _ InvestopediaBitcoin's success has spawned a number of competing cryptocurrencies, such as LiteCoin, NameCoin, PeerCoin, etc.
Satoshi Nakamoto
It is the name used by the unknown creator of the protocol used in the bitcoin cryptocurrency. Satoshi Nakamoto (Japanese) is closely-associated with Bitcoin and the Bitcoin blockchain technology. It used SHA-256, a cryptographic hash function, as its proof-of-work scheme. To date it is unclear if he or she is a single person, or if the name is a moniker used by a group. What is known is that Satoshi Nakamoto published a paper in 2008 that jumpstarted the development of cryptocurrency. It is interesting to note that he never intended to invent a currency. In his announcement of Bitcoin in late 2008, Satoshi said he developed “A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.”Legal Status of Cryptocurrencies
The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies substantially from country to country and is still undefined or changing in many of them. Some countries have explicitly allowed their use and trade while others have banned or restricted it. China Central Bank banned the handling of bitcoins by financial institutions during an extremely fast adoption period in early 2014. In Russia, though cryptocurrencies are legal still it is illegal to actually purchase goods with any currency other than the Russian ruble. On March 25, 2014, the United States Internal Revenue Service ruled that bitcoin will be treated as property for tax purposes as opposed to currency.How Miners Create Coins and Confirm Transactions
A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin consists of a network of peers. Every peer has a record of the complete history of all transactions and thus of the balance of every account. For instance, a transaction is a file that says, “Bob gives X Bitcoin to Alice” and is signed by Bob‘s private key. It‘s basic public key cryptography. After signed, a transaction is broadcasted in the network, sent from one peer to every other peer. This is basic p2p-technology.
As long as a transaction is unconfirmed, it is pending and can be forged. When a transaction is confirmed, it is set in stone. It is no longer forgeable, it can‘t be reversed, it is part of an immutable record of historical transactions: of the so-called blockchain.
Only miners can confirm transactions. This is their job in a cryptocurrency-network. They take transactions, stamp them as legit and spread them in the network. After a transaction is confirmed by a miner, every node has to add it to its database. It has become part of the blockchain.
For this job, the miners get rewarded with a token of the cryptocurrency, for example with Bitcoins. Since the miner‘s activity is the single most important part of cryptocurrency-system we should stay for a moment and take a deeper look on it.
Cryptocurrency – Pros and Cons
Pros

(Image Courtesy: Blockgeeks)
- Cryptocurrencies make it easier to transfer funds between two parties in a transaction; these transfers are facilitated through the use of public and private keys for security purposes. These fund transfers are done with minimal processing fees, allowing users to avoid the steep fees charged by most banks and financial institutions for wire transfers.
- Transactions that occur through the use and exchange of these altcoins are independent from formal banking systems, and therefore can make tax evasion simpler for individuals. Since charting taxable income is based upon what a recipient reports to the revenue service, it becomes extremely difficult to account for transactions made using existing cryptocurrencies, a mode of exchange that is complex and (in some cases) impossible to track.
- Central to the genius of Bitcoin is the block chain it uses to store an online ledger of all the transactions that have ever been conducted using bitcoins, providing a data structure for this ledger that is exposed to a limited threat from hackers and can be copied across all computers running Bitcoin software. Many experts see this block chain as having significant uses in technologies, such as online voting and crowdfunding, and major financial institutions such as JP Morgan Chase see potential in cryptocurrencies to lower transaction costs by making payment processing more effective.
- Cryptocurrencies are not immune to the threat of hacking. In Bitcoin's short history, the company has been subject to over 40 thefts, including a few that exceeded $1 million in value. Still, many observers look at cryptocurrencies as hope that a currency can exist that preserves value, facilitates exchange, is more transportable than hard metals and since these use decentralized control therefore these are outside the influence of central banks and governments.
Cons
- However, because cryptocurrencies are virtual and do not have a central repository, a digital cryptocurrency balance can be wiped out by a computer crash due to malware or data loss or through the destruction of the physical media, effectively removing lost cryptocurrencies forever from their markets if a backup copy of the holdings does not exist.
- Since cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that are managed through advanced encryption techniques, many governments have taken a cautious approach toward them, fearing their lack of central control and the effects they could have on financial security.
- Regulators in several countries have warned against their use and some have taken concrete regulatory measures to deter users.
- Since prices are based on supply and demand, the rate at which a cryptocurrency can be exchanged for another currency can fluctuate widely.
- Compared with ordinary currencies held by financial institutions or kept as cash on hand, cryptocurrencies can be more difficult for seizure by law enforcement.
- Many banks do not offer services for cryptocurrencies and can refuse to offer services to virtual-currency companies.
- Cryptocurrency transactions are normally irreversible after a number of blocks confirm the transaction. One of the features cryptocurrency lacks in comparison to credit cards is consumer protection against fraud, such as chargebacks.
- Also the success of some cryptocurrencies has caused multi-level marketing schemes to arise with pseudo cryptocurrencies, such as OneCoin.
Important Terminologies associated with Cryptocurrency
Miner
Within cryptocurrency systems the safety, integrity and balance of ledgers is maintained by a community of mutually distrustful parties referred to as miners: members of the general public using their computers to help validate and timestamp transactions adding them to the ledger in accordance with a particular timestamping scheme. Miners have a financial incentive to maintain the security of a cryptocurrency ledger.Principally everybody can be a miner. Since a decentralized network has no authority to delegate this task, a cryptocurrency needs some kind of mechanism to prevent one ruling party from abusing it.

Ledger
In September 2015, the establishment of the peer-reviewed academic journal Ledger was announced. It will cover studies of cryptocurrencies and related technologies, and is published by the University of Pittsburgh The journal encourages authors to digitally sign a file hash of submitted papers, which will then be timestamped into the bitcoin blockchain. Authors are also asked to include a personal bitcoin address in the first page of their papersBitcoin Cash
It is a fork of Classical Bitcoin that was created in August 2017. Bitcoin Cash increases the size of blocks, allowing more transactions to be processed.Since its launch, Bitcoin faced pressure from community members on the topic of scalability. Specifically, that the size of blocks – set at 1 megabyte (MB), or 1,000 bytes, in 2010 – would slow down transaction processing times, thus limiting the currency’s potential, just as it was gaining in popularity. The block size limit was added to the Bitcoin code in order to prevent spam attacks on the network at a time when the value of a Bitcoins was low. By 2015, the value of Bitcoins had increased substantially and average block size had reached 600 bytes, creating a scenario in which transaction times could run into delays as more blocks reached maximum capacity. _ Investopedia
Digital Copy
A duplicate record of every confirmed Bitcoin transaction that has taken place over a peer-to-peer network. Digital copy is one of the security features of the Bitcoin platform that was implemented in order to tackle the problem of double spending.Bitcoin Unlimited
A proposed upgrade to Bitcoin Core that allows larger block sizes. Bitcoin Unlimited is designed to improve transaction speed through scale.Double-Spending
The risk that a digital currency can be spent twice. Double-spending is a problem unique to digital currencies because digital information can be reproduced relatively easily. Physical currencies do not have this issue because they cannot be easily replicated, and the parties involved in a transaction can immediately verify the bona fides of the physical currency. With digital currency, there is a risk that the holder could make a copy of the digital token and send it to a merchant or another party while retaining the original. This was a concern initially with Bitcoin, the most popular digital currency since it is a decentralized currency with no central agency to verify that it is spent only once. However, Bitcoin has a mechanism based on transaction logs to verify the authenticity of each transaction and prevent double-counting.
Block Chain
Bitcoin requires that all transactions, without exception, be included in a shared public transaction log known as a block chain. This mechanism ensures that the party spending the bitcoins really owns them, and also prevents double-counting and other fraud. The block chain of verified transactions is built up over time as more and more transactions are added to it. Bitcoin transactions take some time to verify because the process involves intensive number-crunching and complex algorithms that take up a great deal of computing power. It is, therefore, exceedingly difficult to duplicate or falsify the block chain because of the immense amount of computing power that would be required to do so.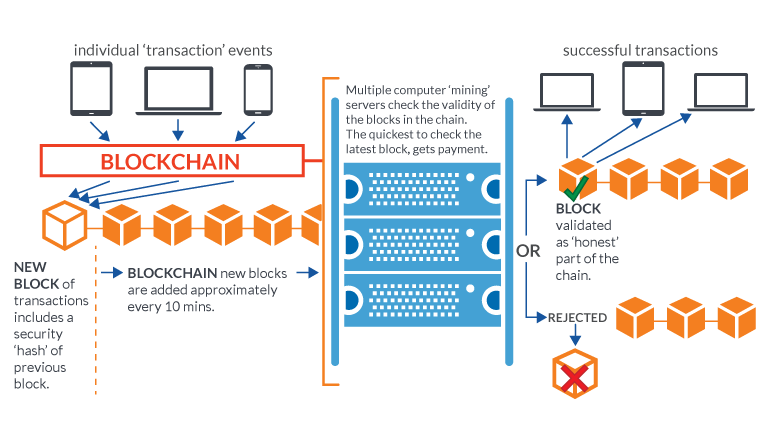 (Image: Open BlockChain)
(Image: Open BlockChain)Altcoin
"Altcoin" is a combination of two words: "alt" and "coin"; alt is short for alternative and coin for currency. Thus together they imply a category of cryptocurrency that is alternative to the digital currency Bitcoin.Altcoins are the alternative cryptocurrencies launched after the success of Bitcoin. Generally, they project themselves as better substitutes to Bitcoin. The success of Bitcoin as the first peer-to-peer digital currency paved the way for many to follow. Many altcoins are trying to target any perceived limitations that Bitcoin has and come up with newer versions with competitive advantages. There is a great variety of altcoins. As of September 2017, there were over 1100 digital currencies in existence.

(Image Courtesy: Blockgeeks)







No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.